Spontaneous Fission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of
 In practice, Pu invariably contains Pu due to the tendency of Pu to absorb an additional neutron during production. Pu's high rate of spontaneous fission makes it an undesirable contaminant. Weapons-grade plutonium contains no more than 7.0% Pu.
The rarely-used gun-type atomic bomb has a critical insertion time of about one millisecond, and the probability of a fission during this time interval should be small. Therefore, only U is suitable. Almost all nuclear bombs use some kind of implosion method.
Spontaneous fission can occur much faster when a nucleus undergoes superdeformation.
In practice, Pu invariably contains Pu due to the tendency of Pu to absorb an additional neutron during production. Pu's high rate of spontaneous fission makes it an undesirable contaminant. Weapons-grade plutonium contains no more than 7.0% Pu.
The rarely-used gun-type atomic bomb has a critical insertion time of about one millisecond, and the probability of a fission during this time interval should be small. Therefore, only U is suitable. Almost all nuclear bombs use some kind of implosion method.
Spontaneous fission can occur much faster when a nucleus undergoes superdeformation.
The LIVEChart of Nuclides - IAEA
'' with filter on spontaneous fission decay {{Nuclear_processes Nuclear physics Nuclear fission Neutron sources Radioactivity
radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
that is found only in very heavy chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s. The nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word ''Atomgewicht'' tomic weight, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approxim ...
of about 56 (e.g., iron-56
Iron-56 (56Fe) is the most common isotope of iron. About 91.754% of all iron is iron-56.
Of all nuclides, iron-56 has the lowest mass per nucleon. With 8.8 MeV binding energy per nucleon, iron-56 is one of the most tightly bound nuclei.
N ...
); spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and a few isolated nuclear particles becomes possible at greater atomic mass numbers.
History
By 1908, physicists understood thatalpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an at ...
involved ejection of helium nuclei from a decaying atom. Like cluster decay, alpha decay is not typically categorized as a process of fission.
The first nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
process discovered was fission induced by neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
s. Because cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s produce some neutrons, it was difficult to distinguish between induced and spontaneous events. Cosmic rays can be reliably shielded by a thick layer of rock or water. Spontaneous fission was identified in 1940 by Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
physicists Georgy Flyorov
Georgii Nikolayevich Flyorov (also spelled Flerov, rus, Гео́ргий Никола́евич Флёров, p=gʲɪˈorgʲɪj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ ˈflʲɵrəf; 2 March 1913 – 19 November 1990) was a Soviet physicist who is known for h ...
and Konstantin Petrzhak
Konstantin Antonovich Petrzhak (alternatively Pietrzak; rus, Константи́н Анто́нович Пе́тржак, p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɐnˈtonəvʲɪtɕ ˈpʲedʐək, ; 4 September 1907– 10 October 1998), , was a Russian physicist ...
by their observations of uranium in the Moscow Metro
The Moscow Metro) is a metro system serving the Russian capital of Moscow as well as the neighbouring cities of Krasnogorsk, Reutov, Lyubertsy and Kotelniki in Moscow Oblast. Opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations, it was the first ...
Dinamo station, underground.
Feasibility
Elemental
Spontaneous fission occurs over practical observation times only for atomic masses of 232 atomic mass units or more. These are nuclei at least as heavy asthorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its decay ...
which has a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable at ...
somewhat longer than the age of the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
. Th, U, and U are primordial nuclides and have left evidence of undergoing spontaneous fission in their minerals.
The known elements most susceptible to spontaneous fission are the synthetic high-atomic-number actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The inform ...
s and transactinide
Superheavy elements, also known as transactinide elements, transactinides, or super-heavy elements, are the chemical elements with atomic number greater than 103. The superheavy elements are those beyond the actinides in the periodic table; the l ...
s with atomic number 100 onward.
For naturally occurring thorium-232, uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exis ...
, and uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it ...
, spontaneous fission does occur rarely, but in the vast majority of the radioactive decay of these atoms, alpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an at ...
or beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For ...
occurs instead. Hence, the spontaneous fission of these isotopes is usually negligible, except in using the exact branching ratios when finding the radioactivity of a sample of these elements, or in applications that are very sensitive to even minuscule numbers of fission neutrons (such as nuclear weapon design
Nuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three existing basic design types:
* pure fission weapons, the simplest and least technically ...
).
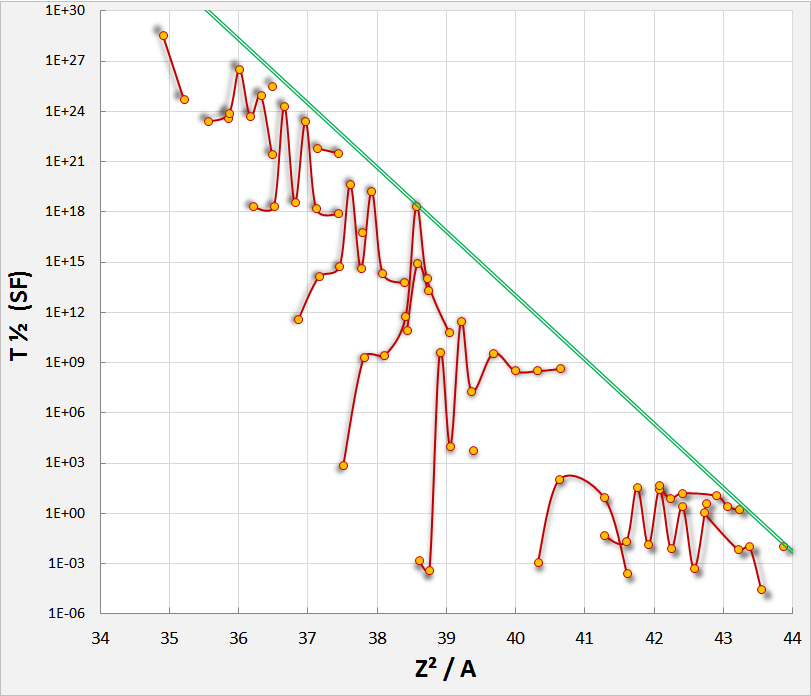
Mathematical
Theliquid drop model
In nuclear physics, the semi-empirical mass formula (SEMF) (sometimes also called the Weizsäcker formula, Bethe–Weizsäcker formula, or Bethe–Weizsäcker mass formula to distinguish it from the Bethe–Weizsäcker process) is used to approxi ...
predicts approximately that spontaneous fission can occur in a time short enough to be observed by present methods when
:
where ''Z'' is the atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
and ''A'' is the mass number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word ''Atomgewicht'' tomic weight, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approxima ...
(e.g., for uranium-235). However, no known radioactive isotope except oganesson-294
Oganesson (118Og) is a synthetic element created in particle accelerators, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first and only isotope to be synthesized was 294Og in 2002 ...
reaches a value of 47 (approximately 47.36), as the liquid drop model is not very accurate for the heaviest known nuclei due to strong shell effects.
Spontaneous fission rates
 In practice, Pu invariably contains Pu due to the tendency of Pu to absorb an additional neutron during production. Pu's high rate of spontaneous fission makes it an undesirable contaminant. Weapons-grade plutonium contains no more than 7.0% Pu.
The rarely-used gun-type atomic bomb has a critical insertion time of about one millisecond, and the probability of a fission during this time interval should be small. Therefore, only U is suitable. Almost all nuclear bombs use some kind of implosion method.
Spontaneous fission can occur much faster when a nucleus undergoes superdeformation.
In practice, Pu invariably contains Pu due to the tendency of Pu to absorb an additional neutron during production. Pu's high rate of spontaneous fission makes it an undesirable contaminant. Weapons-grade plutonium contains no more than 7.0% Pu.
The rarely-used gun-type atomic bomb has a critical insertion time of about one millisecond, and the probability of a fission during this time interval should be small. Therefore, only U is suitable. Almost all nuclear bombs use some kind of implosion method.
Spontaneous fission can occur much faster when a nucleus undergoes superdeformation.
Poisson process
Spontaneous fission gives much the same result as inducednuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
. However, like other forms of radioactive decay, it occurs due to quantum tunneling
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantizati ...
, without the atom having been struck by a neutron or other particle as in induced nuclear fission. Spontaneous fissions release neutrons as all fissions do, so if a critical mass is present, a spontaneous fission can initiate a self-sustaining chain reaction. Radioisotopes for which spontaneous fission is not negligible can be used as neutron sources. For example, californium
Californium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first synthesized in 1950 at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (then the University of California Radiation Laboratory), by bombarding ...
-252 (half-life 2.645 years; SF branch ratio 3.1%) can be used for this purpose. The neutrons released can be used to inspect airline luggage for hidden explosives, to gauge the moisture content of soil in highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
and building construction, or to measure the moisture of materials stored in silos, for example.
As long as the spontaneous fission gives a negligible reduction of the number of nuclei that can undergo such fission, this process can be approximated closely as a Poisson process
In probability, statistics and related fields, a Poisson point process is a type of random mathematical object that consists of points randomly located on a mathematical space with the essential feature that the points occur independently of one ...
. In this situation, for short time intervals the probability of a fission is directly proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constan ...
to the length of time.
The spontaneous fission of uranium-238 and uranium-235 leaves trails of damage in the crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric pat ...
of uranium-containing minerals when the fission fragments recoil through them. These trails, or ''fission tracks'', are the foundation of the radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares t ...
method called fission track dating
Fission track dating is a radiometric dating technique based on analyses of the damage trails, or tracks, left by fission fragments in certain uranium-bearing minerals and glasses. Fission-track dating is a relatively simple method of radiomet ...
.
See also
*Natural nuclear fission reactor
A natural nuclear fission reactor is a uranium deposit where self-sustaining nuclear chain reactions occur. The conditions under which a natural nuclear reactor could exist had been predicted in 1956 by Japanese American chemist Paul Kuroda. ...
Notes
External links
* 'The LIVEChart of Nuclides - IAEA
'' with filter on spontaneous fission decay {{Nuclear_processes Nuclear physics Nuclear fission Neutron sources Radioactivity